Other criteria that influence the operating behavior
The Cox distribution is a distribution with k sequential phases, leaving the operator after each phase can be. A representation of these operating distributions can be found in BOLC chapter.. For interested parties In an approximation method, which has yield distributions for the approximation of empirical SCHM and SCHM and KRAM are recommended for distribution functions. If, however, In which events may occur only in certain queue management time intervals, the memory less geometrical one can be found Distribution to describe the operating behavior. The time is divided into so-called slots. For more information, see previous section Furthermore, events for models with deterministic or generally distributed operating times can be determined.
.jpg?timestamp=1478515599227)
The calculation is usually complicated because the advantage of memorylessness is not given. A table of the most important distributions can be found in the appendix Table D. -D.. Next The density functions are also given the expectation value and variance. In addition to the operating time queue management system price distribution, there are other criteria that influence the operating behavior. There is also the possibility of a condition-dependent operation. Further The number of operators and K the maximum number of customers in the system. The queue discipline Is described by DIS.
.jpg?timestamp=1478515648649)
Depending on the number of queue management system price customers in the system The individual customer is served faster or slower. A switch officer notices how a sheer Endless serpent builds up and hurries either with the check-in, in order to be ready for service or He continues the work disheartened, since the queue is not getting smaller. Further, there is the possibility of group operation, i. An operator manufactures several customers at once from. Two cases must be distinguished. On the one hand there is the possibility that the operator also fewer Customers together when it is possible, on the other hand it waits until so many customers have arrived, That a full group can be served.
What Exactly Is Happening With queue management system price
The queue discipline specifies the way the individual customers are queuing out For operation. The most important disciplines are described and described as follows: First-Come-First-Served FCFS or FIFO First-In-First-Out The customers are served in the order of their arrival. LCFS Last-Come-First-Served or LIFO Last-In-First-Out The last arrived customer is served first. This discipline is suitable for modeling Stacking queue management system problems. RSS Random Selection-For-Service or SIRO Service-In-Random-Order The next customer from the queue is randomly selected. PRI Priority The individual customers are assigned to a certain priority class.
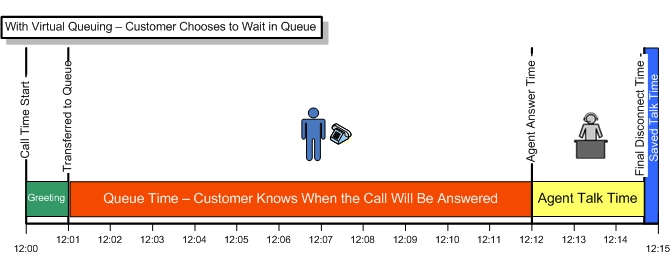
Customers of a higher Priority class is preferred to a lower priority class. For customers with the same Priority is given to FCFS. Furthermore, the following priority functions are distinguished: In the preemptive case, a customer with Higher priority, push a customer of lower priority out of the control unit to equal the same To be dealt with. The repressed customer is returned to the Queue. In the non-preemptive case, the customer with the highest priority in Of the queue in the first place. Especially interesting lately are the Dynamic priorities. Notation For the description of simple queuing systems, the following reference has been made to D. G. Kendall returning Brief description. A denotes the distribution of the intermediate arrival times and B the distribution of the operating times.
.jpg?timestamp=1478515758367)
The priorities change as a function of time. RR round robin A customer is operated within a specified time interval. Exceeds the total operating time of the customer is the length of this interval, this becomes the last point of an FSFS queue Intercepted This strategy is, for example, the modeling of synchronous Multiplexers.. System capacity On many models, there is limited space available. If the system capacity memory space capacity Customers in operation, new arriving customers are rejected. This situation describes inter Asia.

Also, the simplest form of an inhibited customer. Once reached the limit The system is not entered.. Number of operators If a system has several operating units, two cases have to be distinguished. On the one hand The control channels have a common queue, and each channel has its own queue. Particularly interesting in the context of queuing networks is the composition of the operating stages. As already mentioned, sequentially click here arranged operators with exponentially distributed operating times can be selected An empirically and hypo exponentially distributed operator. For a variety of models is But not an aggregated distribution of the individual operating time distributions. Such queuing networks Can be analyzed with suitable algorithms..